Decision Environments
Decision making Environments:
To achieve a Decision theoretic solution (an optimized decision), a decision maker needs to do some sequential processes which are given below:
Here there is complete information about future and only one state of nature exists. So, it is easy to choose a most optimal alternative.
Here the information about the probability of future events is not sufficient and there are more than one states of nature.
Here there is complete information about the probability of future events and also more than one states of nature exist.
I. Decision making under conditions of certainty:
Since there is only one state of nature, the decision maker simply chooses his best payoff in that state of nature and opt out the respective alternative.
For example, if the company knew that the demand would be high, it would choose the alternative ‘Construct’ to get the highest payoff;
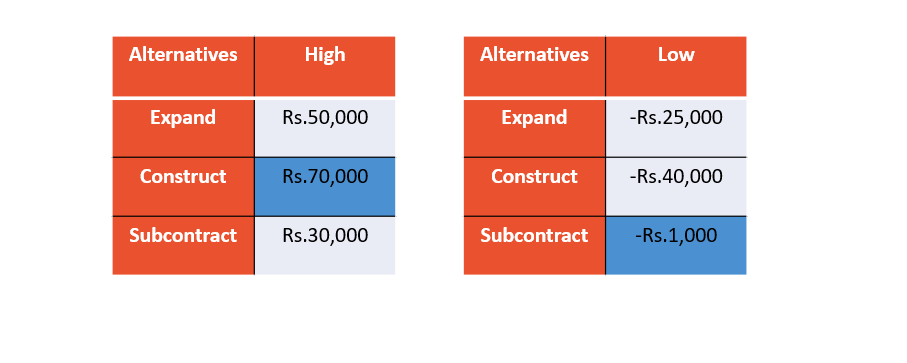
If it knew that the demand would be low, it would choose the alternative ‘Subcontract’ to get the lowest loss;
Under conditions of certainty, since there is only one state of nature that particular state of nature will have probability 1. But there may be a number of alternatives exist for this single state of nature. Linear programming, transportation and assignment techniques, input-output analysis, activity analysis and EOQ models are used in these situations.
II. Decision making under conditions of Uncertainty:
Under conditions of uncertainty, the decision maker knows all states of nature but not their occurrence probabilities. Launching new product comes under this category.
Decisions taken under these circumstances will not be satisfactory because of this data insufficiency. However, the decision maker may choose scientific methods to exploit the available data to the maximum.
Under conditions of uncertainty, a decision maker may follow any one of the criterions given below to get an optimized decision.
- Maximax Criterion (Optimistic criterion)
- Maximin Criterion (Pessimistic criterion)
- Minimax Regret Criterion
- Hurwicz Criterion (Criterion of Realism)
- Laplace Criterion (Criterion of Rationality)